Cirrhosis In India
About Cirrhosis ?
Cirrhosis is a condition in which the liver does not function properly due to long-term damage. Typically, the disease comes on slowly over years. Early on, there are often no symptoms. As the disease worsens, a person may become tired, weak, itchy, have swelling in the lower legs, develop yellow skin, bruise easily, have fluid build up in the abdomen, or develop spider-like blood vessels on the skin. The fluid build-up in the abdomen may become spontaneously infected.
Other complications include hepatic encephalopathy, bleeding from dilated veins in the esophagus or dilated stomach veins, and liver cancer. Hepatic encephalopathy results in confusion and possibly unconsciousness.
Signs and symptoms
Cirrhosis has many possible manifestations. These signs and symptoms may be either as a direct result of the failure of liver cells or secondary to the resultant portal hypertension. There are also some manifestations whose causes are nonspecific, but may occur in cirrhosis. Likewise, the absence of any does not rule out the possibility of cirrhosis.Cirrhosis of the liver is slow and gradual in its development. It is usually well advanced before its symptoms are noticeable enough to cause alarm. Weakness and loss of weight may be early symptoms.
Liver dysfunction
Spider angiomata or spider nevi are vascular lesions consisting of a central arteriole surrounded by many smaller vessels (hence the name "spider") and occur due to an increase in estradiol. One study found that spider angiomata occur in about 1/3 of cases.
Palmar erythema is a reddening of palms at the thenar and hypothenar eminences also as a result of increased estrogen
Gynecomastia, or increase in breast gland size in men that is not cancerous, is caused by increased estradiol and can occur in up to 2/3 of patients.This is different from increase in breast fat in overweight people.
Hypogonadism, a decrease in sex hormones manifest as impotence, infertility, loss of sexual drive, and testicular atrophy, can result from primary gonadal injury or suppression of hypothalamic/pituitary function. Hypogonadism is associated with cirrhosis due to alcoholism and hemochromatosis.
Cirrhosis
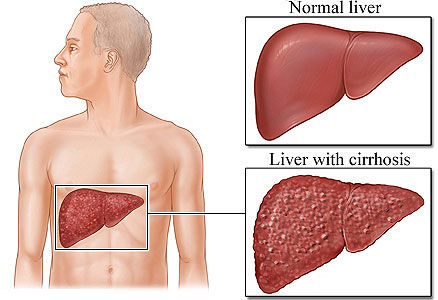
Advanced disease
As the disease progresses, complications may develop. In some people, these may be the first signs of the disease.
Bruising and bleeding resulting from decreased production of coagulation factors.
Hepatic encephalopathy - the liver does not clear ammonia and related nitrogenous substances from the blood, which are carried to the brain, affecting cerebral functioning: neglect of personal appearance, unresponsiveness, forgetfulness, trouble concentrating, or changes in sleep habits. This can be seen on exam by asterixis which is bilateral asynchronous flapping of outstretched, dorsiflexed hands seen in patients with hepatic encephalopathy.
Sensitivity to medication caused by decreased metabolism of the active compounds.
Acute kidney injury (particularly hepatorenal syndrome)
Diagnosis
The gold standard for diagnosis of cirrhosis is a liver biopsy, through a percutaneous, transjugular, laparoscopic, or fine-needle approach. A biopsy is not necessary if the clinical, laboratory, and radiologic data suggests cirrhosis.