Endoscopic Surgery in India
What is Endoscopic ?
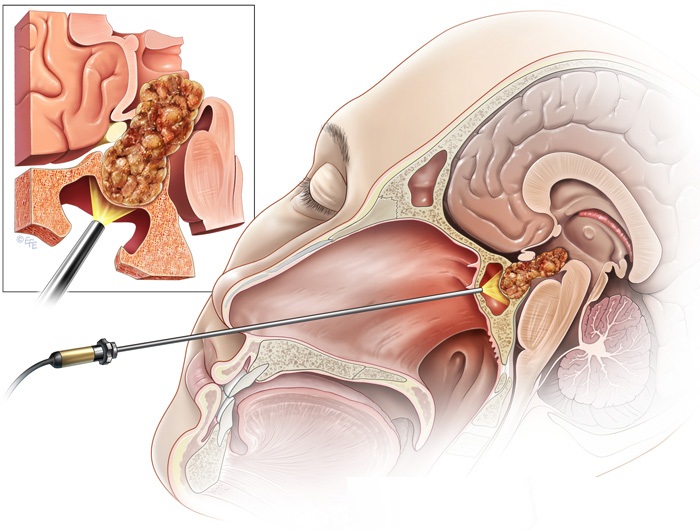
Endoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive technique used mainly in neurosurgery and otolaryngology. A neurosurgeon or an otolaryngologist, using an endoscope that is entered through the nose, fixes or removes brain defects or tumors in the anterior skull base. Normally an otolaryngologist performs the initial stage of surgery through the nasal cavity and sphenoid bone; a neurosurgeon performs the rest of the surgery involving drilling into any cavities containing a neural organ such as the pituitary gland.
Endoscopic Instrumentation
The endoscope consists of a glass fiber bundle for cold light illumination, a mechanical housing, and an optics component with four different views: 0 degree for straight forward, 30 degrees for forward plane, 90 degrees for lateral view, and 120 degrees for retrospective view.For endoscopic endonasal surgery, rigid rod-lens endoscopes are used for better quality of vision, since these endoscopes are smaller than the normal endoscope used colonoscopies.
Endocrinology
An endocrinologist is only involved in preparation for an endoscopic endonasal surgery, if the tumor is located on the pituitary gland. The tumor is first treated pharmacologically in two ways: controlling the levels of hormones that the pituitary gland secretes and reducing the size of the tumor. If this approach does not work, the patient is referred to surgery. The main types of pituitary adenomas are:
PRL-secreting or prolactinomas: These are the most common pituitary tumors. They are associated with infertility, gonad, and sexual dysfunction because they increase the secretion of prolactin or PRL. One drug that endocrinologist use is bromocriptine (BRC), which normalizes PRL levels and has been shown to lead to tumor shrinkage. Other drugs to treat prolactinomas include quinagolide (CV) or cabergoline (CAB) acting as dopamine (D2) antagonists. Endoscopic endonasal surgery is normally performed as a last resort when the tumor is resistant to the drugs, shows no tumor shrinkage, or the PRL levels cannot be normalized.
ACTH-secreting: This tumor is a result of the increase in the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and leads to Cushing's syndrome. Pharmacology has little effect and therefore surgery is the best option. Removal of the tumor results in an 80%-90% cure rate.
Endoscopic
Neuroradiology
A neuroradiologist takes images of the defect so that the surgeon is prepared on what to expect before surgery. This includes identifying the lesion or tumor, controlling the effects of the medical therapy, defining the spatial situation of the lesions, and verifying the removal of the lesions.The lesions associated with endoscopic endonasal surgery include:
Pituitary microadenomas
Pituitary macroadenomas
Rathke's cleft cysts
Ophthalmology
Some suprasellar tumors invade the chiasmatic cistern, causing impaired vision. In these cases, an ophthalmologist maintains optic health by administering pre-surgical treatment, advising proper surgical techniques so that the optic nerve is not in danger, and managing post-surgery eye care. Common problems include:
Visually evoked potential (VEP) abnormalities