Lung Cancer in India
What is Lung Cancer ?
Lung Cancer, also known as carcinoma of the lung or pulmonary carcinoma, is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung by process of metastasis into nearby tissue or other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in the lung, known as primary lung cancers, are carcinomas that derive from epithelial cells. The main primary types are small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) and non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC).
Causes
Cancer develops following genetic damage to DNA and epigenetic changes. These changes affect the normal functions of the cell, including cell proliferation, programmed cell death (apoptosis) and DNA repair. As more damage accumulates, the risk of cancer increases.
Smoking
Smoking, particularly of cigarettes, is by far the main contributor to lung cancer.Cigarette smoke contains at least 73 known carcinogens,including benzo[a]pyrene, NNK, 1,3-butadiene and a radioactive isotope of polonium, polonium-210.Across the developed world, 90% of lung cancer deaths in men during the year 2000 were attributed to smoking (70% for women).Smoking accounts for 80–90% of lung cancer cases.
Diagnosis
Performing a chest radiograph is one of the first investigative steps if a person reports symptoms that may suggest lung cancer. This may reveal an obvious mass, widening of the mediastinum (suggestive of spread to lymph nodes there), atelectasis (collapse), consolidation (pneumonia) or pleural effusion.
Mastectomy: Removal of the whole breast.
Quadrantectomy: Removal of one quarter of the breast.
Lumpectomy: Removal of a small part of the breast.
Lung cancer often appears as a solitary pulmonary nodule on a chest radiograph. However, the differential diagnosis is wide. Many other diseases can also give this appearance, including tuberculosis, fungal infections, metastatic cancer or organizing pneumonia. Less common causes of a solitary pulmonary nodule include hamartomas, bronchogenic cysts, adenomas, arteriovenous malformation, pulmonary sequestration, rheumatoid nodules, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, or lymphoma.
Lung Cancer
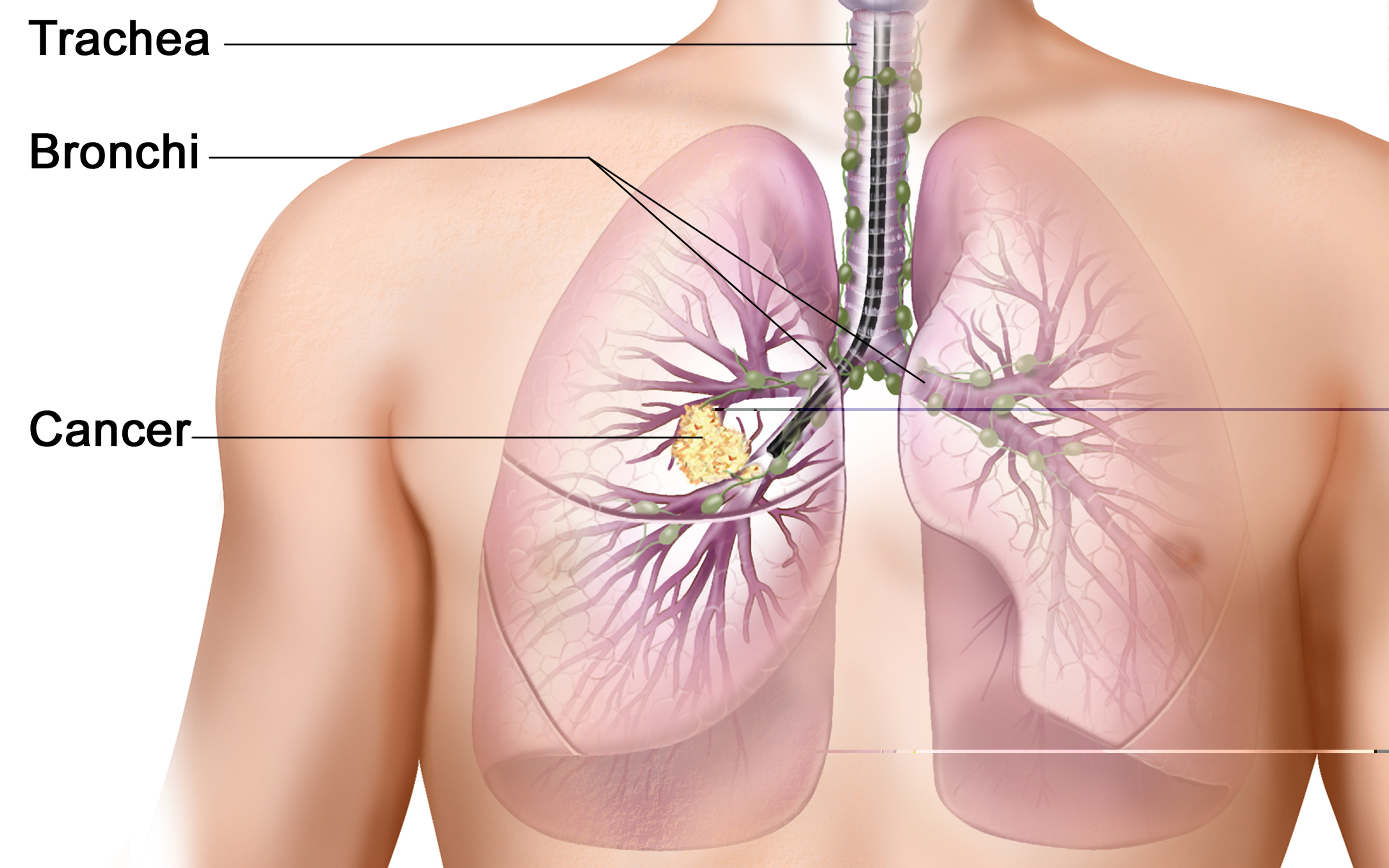
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms which may suggest lung cancer include:
Respiratory symptoms: coughing, coughing up blood, wheezing or shortness of
Systemic symptoms: weight loss, fever, clubbing of the fingernails, or fatigue.
Symptoms due to the cancer mass pressing on adjacent structures: chest pain, bone pain, superior vena cava obstruction, difficulty swallowing.
Surgery
If investigations confirm NSCLC, the stage is assessed to determine whether the disease is localized and amenable to surgery or if it has spread to the point where it cannot be cured surgically. CT scan and positron emission tomography are used for this determination. If mediastinal lymph node involvement is suspected, mediastinoscopy may be used to sample the nodes and assist staging.
In most cases of early-stage NSCLC, removal of a lobe of lung (lobectomy) is the surgical treatment of choice. In people who are unfit for a full lobectomy, a smaller sublobar excision (wedge resection) may be performed. However, wedge resection has a higher risk of recurrence than lobectomy.