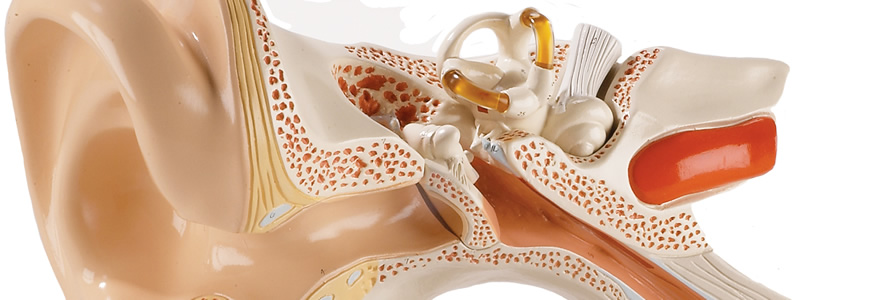
Surgical Approach
Tympanoplasty can be performed through the ear canal (trascanal approach), through an incision in the ear (endaural approach) or through an incision behind the ear (postauricular approach).
A graft may be taken to reconstruct the tympanic membrane. Common graft sites include the temporalis fascia and the tragus.
The surgery takes ½ to 1 hour if done through the ear canal and 2⅓ to 3 hours if an incision is needed. It is done under local or general anesthesia. It is done on an inpatient or day case basis and is successful 85-90% of the time.