Uterine Cancer in India
About Uterine Cancer ?
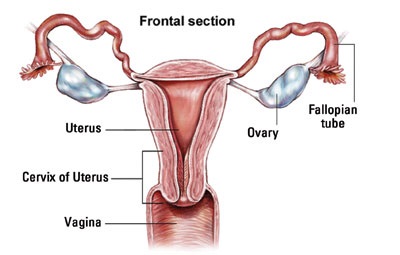
Uterine cancer or womb cancer is any type of cancer that emerges from the tissue of the uterus. It can refer to several types of cancer, with cervical cancer (arising from the lower portion of the uterus) being the most common type worldwide and the second most common cancer in women in developing countries.Endometrial cancer (or cancer of the inner lining of the uterus) is the second most common type, and fourth most common cancer in women from developed countries.Risk factors depend on specific type, but obesity, older age, and human papillomavirus infection add the greatest risk of developing uterine cancer.
It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body.Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, and feeling tired all the time.
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of colorectal cancer depend on the location of the tumor in the bowel, and whether it has spread elsewhere in the body (metastasis). The classic warning signs include: worsening constipation, blood in the stool, decrease in stool caliber (thickness), loss of appetite, loss of weight, and nausea or vomiting in someone over 50 years old.
Causes
Greater than 75-95% of colon cancer occurs in people with little or no genetic risk.Other risk factors include older age, male gender,high intake of fat, alcohol or red meat, obesity, smoking, and a lack of physical exercise.Approximately 10% of cases are linked to insufficient activity.
Surgery
If the cancer is found at a very early stage, it may be removed during a colonoscopy.For people with localized cancer, the preferred treatment is complete surgical removal with adequate margins, with the attempt of achieving a cure. This can either be done by an open laparotomy or sometimes laparoscopically.The colon may than be reconnected or a person may have a colostomy.
Uterine Cancer
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of colorectal cancer is via sampling of areas of the colon suspicious for possible tumor development typically done during colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, depending on the location of the lesion. The extent of the disease is then usually determined by a CT scan of the chest, abdomen and pelvis. There are other potential imaging test such as PET and MRI which may be used in certain cases. Colon cancer staging is done next and based on the TNM system which is determined by how much the initial tumor has spread, if and where lymph nodes are involved, and the extent of metastatic disease.
The microscopic cellular characteristics of the tumor are usually reported from the analysis of tissue taken from a biopsy or surgery. A pathology report will usually contain a description of cell type and grade.